
The Deneb Star– Facts in brief:
What is it?
Deneb is a blue-white supergiant star, of spectral type A2 Ia, located in the Constellation Cygnus (associated with the image of a Swan). Deneb (alpha Cygni) is the brightest star in the Constellation Cygnus, and one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
It has an average apparent magnitude of 1.25, making it a first magnitude Star, and it is 196,000 times more luminous than the Sun. The proper name of this supergiant star is Deneb (from Arabic) and it is also referred to as Alpha Cygni, a Cyg and 50 Cyg.
As this bright star has grown over time it now has now reached a radius of 203 solar radii, which makes it 19 times more massive than the Sun.
Part of the asterisms – the ‘Northern Cross’ and the ‘Summer Triangle’
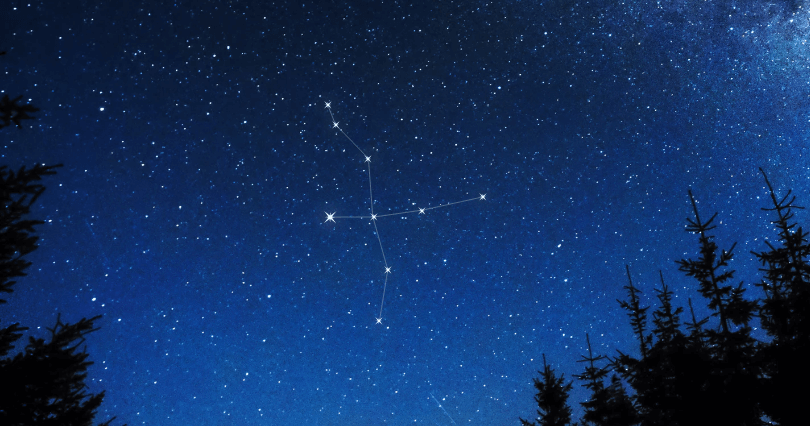
Deneb is one of the bright stars within the well-known ‘Northern Cross’ asterism, and it also forms part of the vertices of the ‘Summer Triangle’ asterism, both within the scope of the Constellation Cygnus.
The Summer Triangle asterism is larger than the Northern Cross and is made up of three first magnitude stars –
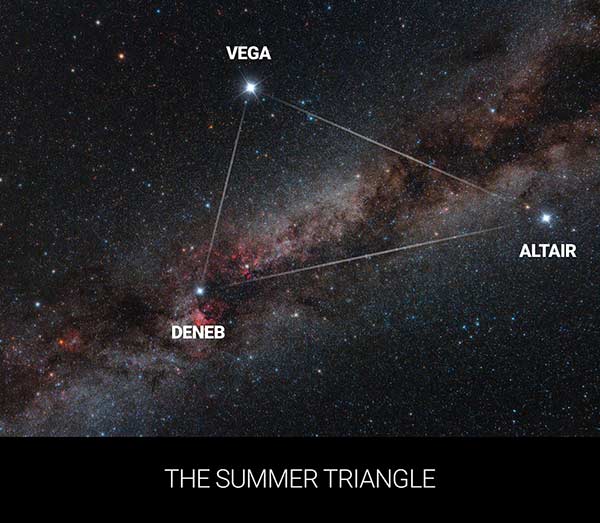
- Deneb (alpha Cygni) – in Constellation Cygnus (the Swan)
- Vega (alpha Lyrae) – in Constellation Lyra (the Lyre)
- Altair (alpha Aquilae) – in Constellation Aquila (the Eagle)
Each of these 3 bright stars make up one vertex of the Summer Triangle.
The bright star Deneb is believed to be the head point of the Northern Cross (in the Northern Hemisphere)
Characteristics
This bright supergiant star is listed as the 19th brightest star in the night sky and is visible by the naked eye. Deneb is classified as a rare A2Ia spectral type white supergiant star.
The latest estimate in 2007 for this blue-white supergiant star locates it around 1425 light years from Earth (436.91 parsecs), although its exact distance is not certain as this is one of the distant starslocated in a remote area of the sky.
FACT: 1 light year equals 0.3066 parsecs
It is a main sequence star that ranks as the brightest star within the Constellation Cygnus that is located in the Northern Hemisphere and crosses the Milky Way. According to the Hipparcos 2007 apparent magnitude list, it has an apparent magnitude of 1.25; making it one of the brightest stars in the Milky Way.
The Star Deneb is also referred to by other names, such as, Deneb Kaitos (incorrectly) and alpha Cygni.
Alpha Cygni is a type of variable star, which means its brightness can vary or fluctuate over time. It is regarded as the main star in a group of variable stars, known as the ‘alpha Cygni variables’.
How was it named?
Deneb is sometimes mistakenly referred to as Deneb Kaitos, which is a different star located in the Constellation of Cetus.
Johann Bayer

In 1603, The German Astronomer – Johann Bayer, systematically assigned names to the brightest stars in each constellation and cataloged them in his Star atlas – ‘Uranometria Omnium Asterismorum’.
The Bayer designations are stellar designations where the stars within Constellations such as the Constellation Cygnus are initially identified by a name or a letter from the Greek Alphabet from Alpha through Omega (in order of brightness).
1. The names of the Stars begin with a letter of the Greek alphabet starting with– Alpha, then beta, gamma, etc.
2. Followed by the genitive form of their parent constellation’s Latin name – ‘Cygni’, sometimes abbreviated to ‘Cyg’
3. The first Star and brightest star in Cygnus is named Alpha Cygnus
The main sequence stars of Cygnus, the Swan Constellation, are named by their apparent magnitude (luminosity) from Earth, listed from the brightest to faintest star in decreasing order:
1. Deneb, (name from Arabic), alpha Cygni – the brightest star with a visual/apparent magnitude of 1.25 (the only first magnitude star in the Cygnus Swan image)
2. Sadr, (name from Arabic) Gamma Cygni– second brightest Star with a visual/apparent magnitude of 2.23, (a suspected variable star)
3. Aljanah, Epsilon Cygni– the third brightest star with a variable magnitude of 2.48
4. Fawaris, (name from Arabic) Delta Cygni – the fourth brightest star with an apparent magnitude of 2.86 (one part of the Northern Cross asterism)
5. Albireo A, a double star, binary Star, with Albireo B, with a visual magnitude of 3.05
Where did the name come from?
The name Deneb, Dhaneb or Dhanab, is from Arabic and means ‘the tail, and Dhanab al Dajajah, means ‘the tail of the bird’,or ‘the tail of the hen’. This is possibly in reference to the location of this bright Star in the outline of the Swan, which we believe represents the Constellation Cygnus, in the Northern Hemisphere.
The traditional name “Deneb’,for the Star alpha Cygni, has been officially recognized by the international Astronomical Union (IAU)
Different versions of the word ‘Deneb’ are used to name stars in other Constellations that are represented by animals:
- Constellation Cetus (the Whale) – Deneb Kaitos
- Constellation Leo (the Lion) – Denebola
Properties of the Deneb Star
The Deneb Star is an extremely luminous and massive star and the brightest star in the Constellation Cygnus.
- Rigel (Beta Orionis), is the most luminous first magnitude star overall, with a highly luminous apparent magnitude of 0.120
Deneb is located –
- South of the Constellation Cepheus
- West of the Constellations Draco and Lyra
- East of the Constellation Lacerta
- North of the Constellation Vulpecula
Deneb is circumpolar, meaning it is visible all year round from locations or 45 degrees north.
It constantly circles round the pole Star.
Mass
The mass of the Deneb Star thought to be around 19 times the mass of the sun, referred to as its stellar mass, and enumerated as the Sun’s mass as a proportion of solar mass.
Radius
Deneb Star was originally thought to have a solar radius of 203 times that of the Sun (written as 203 R).
How bright is this Deneb Star
The Deneb Star is a blue-white supergiant star (c LBV) and is estimated to be the 19th most luminous star of all the known stars.
Its luminosity is the amount of energy emission from this giant star relative to the Sun. It is estimated to between 55,000 to 196,000 times brighter than the Sun.
The brightness of a star as seen from earth is measured by its magnitude of which there are three classifications: Apparent Magnitude, Visual Magnitude and Absolute Magnitude.
The measurements for the brightness of the Deneb Star are:
- An apparent magnitude of +1.25 (also referred to as its visual magnitude)
- An absolute magnitude of -8.38
FACT: The Apparent Magnitude is how bright we see a Star from Earth, and the Absolute Magnitude is the Apparent Magnitude of that star from a 10 parsecs distance (32.6 light years), assuming there are no molecular clouds, or dust in the line of sight.
The lower the number of magnitude the brighter the Star.
The color of the Deneb Star
The Deneb Star is classified as a variable type of Star, which according to the spectral type of this star, A2Ia, classifies it as a blue-white supergiant colored Star.
It began life as an O-type main-sequence star, although it has exhausted the hydrogen in its core and has now expanded to become a supergiant.
Most stars in the mass range of Deneb expand to become red Supergiants and eventually, after a few million years, collapse in a supernova explosion
The temperature of this blue supergiant
Based on the spectral type of this Star it is estimated to be at least 8,500 degrees Kelvin. This makes it one of the hotter Stars in the Universe.
Where is it located? –
Deneb is the most distant star of the 30 brightest stars, by a factor of 2.
The distances vary depending on how it’s measured and there are certainly margins of error.
According the latest 2007 Hipparcos measurement the parallax data gave an uncertain result. The Deneb Star is estimated to be around 1411.96 light years (432.90 parsecs) from Earth.
FACT: A parallax is a difference in the apparent position of a star or any solar system object viewed from two different lines of sight. The parallax is measured by the angle between the two lines of sight.
The distance between the Earth and the Sun is known as an Astronomical Unit.
The figure of A.U. is calculated as the number of times that Star is from Earth, in relation to the Sun. It is estimated that the Deneb Star is approximately 89,291,412,43 A.U. from an Earth to Sun distance.
FACT: All Stars and Planets orbit round a central point, the planets orbit the Sun and the Stars orbit the Galactic Centre.
The Star Deneb is located approximately 25,075.44 light years from the Galactic Center, the center of the galaxy we call the Milky Way.
The Galacto-Centric distance is measured as the distance from that Star to the center of the Galaxy (Sagittarius A).
Fact: the Galactic Center, or Galactic Centre, is a supermassive black hole and the rotational center of our Milky Way galaxy. It is not possible to view it at visible, ultraviolet, or even soft or low-energy X-ray wavelengths because of the molecular clouds of interstellar dust along its line of sight.

Where can it be seen?
The Deneb Star is one of the 5 main Stars in the outline of the Constellation Cygnus and one of the most distant stars you can see by the naked eye.
The luminous Deneb Star is of great interest to amateur astronomers as it forms part of the famous Summer Triangle asterism.
Deneb, Vega and Altair (named from the Arabic language) are the three first magnitude Stars that make up this well-known asterism spanning 3 Constellations Cygnus, Lyra and Aquila.
Finding the Summer Triangle is the easiest way to spot Deneb.
Co-ordinates of a right ascension, or left ascension and their declination are used to locate all of the notable objects in the sky
The Deneb Star lies at a 20 hours 41 minute right ascension,and a declination of +45 degrees.
The right ascension – is the angular distance of any sky object along the celestial equator from the March (Spring) equinox.
- If it has a positive number it is east of the March equinox.
The declination – is the angle of the sky object from the celestial equator.
- If it has a positive number it indicates it is located in the Northern Hemisphere
The age of the Deneb Star
It is not certain what age the Deneb Star is or how long it is likely to continue to survive.
One estimate of the age of this Star, is around 10 million years.
How can you identify the Deneb Star?
The simplest method for spotting any particular Star from Earth is to first of all locate an easy to recognize neighboring Constellation or object in the night sky.
The Constellation Cygnus would be a good starting location for finding the Deneb Star.
The Deneb star is a part of the Constellation of Cygnus and the best time of year to spot it is late Spring until May in the Northern Hemisphere.
Like all stars, Deneb is constantly on the move and moves about one degree in a Westerly direction, at the same time every day.
Deep Sky Objects
FACT: A Deep Sky Object is an astronomical object, that is not a solar system object like the Sun, Moon, Comet or a Planet.
Individual Stars, such as Alnitak, Mintaka and Alnilam are not considered to be Deep Sky Objects.
Deep Sky Objects are faint objects that can still be observed by the naked eye in the night sky from Earth.
Deep Sky Objects include Galaxies, Star Clusters and Nebulae.
- Star clusters – such as Globular Clusters of Stars or Open Clusters of Stars
- Dark Nebula, Planetary Nebula, Diffuse Nebula, and Supernova remnants
- Galaxy Groups, Galaxies, Spiral Galaxies, Gravitational Lenses and Quasars
How do we obtain the images and measurements of Stars from Space?
Images of the different Stars and nebulae have been captured using a professional large telescope, such as the NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, with a near infrared camera and multi-object spectrometer.
The standard measurement of distance for Stars for decades has been using the ESA Earth-orbiting Hipparcos satellite, which replaced the ESA Gaia mission to chart a three dimensional map of the Milky Way galaxy.
ESA Gaia measured the positions and radical velocities of around one billion stars in our galaxy.
Fun Facts about Stars – Did you know that?
- The Northern Cross is not officially listed as an asterism, although it is a collection of stars in one area.
- The Star we call The Sun does not belong to any constellation
- The planet Jupiter is often cited when making size comparisons between planets or stars. The Jupiter mass is a unit of mass equal to the total mass of planet Jupiter
- The rate of formation of stars in a starburst galaxy is more than 10 times faster than the star formation in the Milky Way galaxy
- The center of a Galaxy does not contain a Giant Star it contains a Supermassive Black Hole.
- A Red Dwarf is not a Dwarf Planet it is a Star. Most common Stars are Red Dwarf (cool Stars)
Commonly Asked Questions
Q. What prevents us seeing the Stars in the night sky?
A. Light pollution, fog, city lights and artificial lights all limit our visibility of the objects in the sky at night.
Q. Will the locations of Stars change over time?
A. Stars are continually on the move.
The images we form in our imagination to make objects, shapes and patterns out of the constellations have already shifted over time.
As we view the night skies from Earth they are likely to continue to shift and possibly in time the images may look very different.
SOURCES:
- Deneb star : Fred Espenak – https://www.astronomytrek.com/star-facts-deneb
- Summer triangle – https://astrobackyard.com/the-summer-triangle
- Nebula – By Credit: NASA, Jeff Hester, and Paul Scowen (Arizona State University) – Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=129538
- Johann Bayer – https://laexuberanciadehades.files.wordpress.com/2012/10/johann-bayer.jpg