The Bellatrix star can be viewed with the naked eye. It marks the left shoulder of Orion and is one of the seven bright stars that outline the celestial Hunter’s hourglass figure. It is also sometimes known as the Amazon Star.

The name Bellatrix comes from the Latin bellātrix, meaning “female warrior.” The name was first mentioned in the works of the 9th century Persian astronomer Abu Maʿshar and their translations from Arabic into Castilian by John of Seville in the 12th century. In Abu Ma’shar’s writings, the name was given to Capella, but was switched to Gamma Orionis by the Vienna school of astronomers in the 15th century.
It is often thought that the name Amazon Star is a loose translation of the star’s Arabic name, Al Najid, meaning “the conqueror”, which appeared in the works of the 13th century Persian astronomer Zakariya al-Qazwini. The 15th century Timurid astronomer Ulugh Beg called the star Al Murzim al Najid, or “the roaring conqueror”, and the 17th century English orientalist Thomas Hyde referred to it as the Conquering Lion.
The Chinese know Bellatrix as the Fifth Star of Three Stars, referring to the Chinese Three Stars asterism. These originally only included Orion’s Belt stars Alnilam, Alnitak and Mintaka, but was later expanded to include additional Orion stars.
The star name Bellatrix was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) on June 30, 2016.
Bellatrix Star – Location and Distance
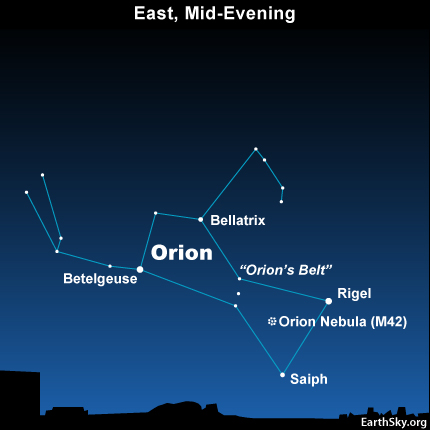
Bellatrix is located in the constellation of Orion, around 250 light years away from Earth. It is one of the four Orion stars selected for navigation. The other three navigational stars in the constellation are the supergiants Rigel, Betelgeuse and Alnilam.
It is very easy to find because it is bright and part of one of the most familiar shapes in the night sky. It marks the left shoulder of Orion appearing right from our perspective, and is located about 5 degrees west (or right) of Betelgeuse. The best time of year to see Bellatrix and other Orion stars is during the month of January, when the constellation dominates the evening sky.
Bellatrix was once believed to belong to the Orion OB1 association, like the stars of Orion’s Belt, but because it only lies 250 light years away, it is much closer to us than Orion OB1 stars, which lie at distances of over 1,000 light years.
Bellatrix Star System and Size
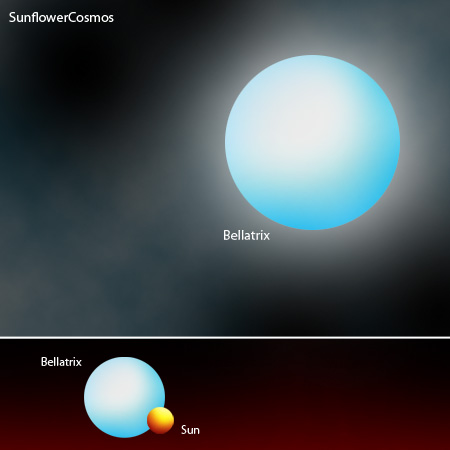
Bellatrix is a bluish main sequence star with the stellar classification B2 V. Some sources cite the spectral type of a giant, B2 III. It has a mass that is 8.6 times that of the Sun and a radius that is 5.75 times that of the Sun. It shines with a luminosity that is 9,211 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 21,700 Kelvin.
With a mass that is 8.6 times that of the Sun, Bellatrix is close to being a supernova candidate, but is not quite massive enough to end its life in a supernova explosion. It will probably end up expelling its outer layers to form a planetary nebula, leaving behind a hot white dwarf to illuminate the expanding shell of gas.
The star is 25.2 million years old and so it won’t be long before it runs out of its supply of hydrogen and evolves into a subgiant and then into an orange giant star.
In 2011, a study was published that identified Bellatrix as double-lined, which suggests that it may be a spectroscopic binary system. However, observations carried out the same year did not find any potential companions that share a proper motion with the star.
History and Composition
Bellatrix once served as a spectral and photometric standard, but the star’s properties have been shown to be undependable.
In 1963, it was one of the bright stars that was used to define the UBV photometric system, which is used for classifying stars based on their colours. It was also used as a spectral standard for the spectral class B2 III as part of an effort to create a reference frame for the classification of class O and early B stars. However, an analysis of the star’s properties has shown it to be a main sequence star (V), not a giant (III).
Bellatrix is linked to many lores across different cultures. The Inuit understood Betelgeuse and Bellatrix as Akuttujuuk, which means “those (two) placed far apart”. The two stars marked the coming of spring and the return of daylight in Arctic latitudes. Together with Meissa, the three stars were also the Euphratean Constellation of the King, or Kakkab Sar, which was believed to bring good fortune, wealth and military honours.
Bellatrix represented a Young Boy in a Canoe chasing a dark spot, Peixie Boi, in the sky with an old man, represented by Betelgeuse, in Amazon River lore. In the Northern Territory of Australia, the Wardaman people called the star Banjan. The star symbolized the sparkling pigment used in ceremonies led by Unumburrgu, the Red Kangaroo Leader, represented by the brighter Rigel.
IMAGE SOURCES:
- Bellatrix Star image – https://50a8d2.medialib.edu.glogster.com/udNPiL04rl02Zj0X0F8f/media/3a/3a1669406cf288d8d548712202544baffeb3928d/rigel-and-sun.jpg
- Location of Bellatrix – https://earthsky.org/upl/2011/12/11Dec01_4302.jpg
- Bellatrix size comp – https://earthandstarryheaven.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/025_bellatrix.jpg