A constellation, including the Scorpius Constellation, is an area on the celestial sphere (an imaginary sphere) where a group of visible stars are located.
These stars typically form a pattern or outline, which we perceive to represent an inanimate object, (like a fish hook or question mark), an animal (like a scorpion,) a mythical person (like Orion, the mythical hunter, from Greek mythology) or even a type of creature (a Gorgon)
It is also an astronomy term used to describe a variety of groups of stars that have been given a specific name such as
Constellations are constantly moving and move in the direction from East to West.

The Constellation Scorpius– Facts in brief:
What is it? –
The Constellation Scorpius (Scorpio) is an ancient Constellation and one of the 12 constellations of the zodiac; it ranks as the 33rd largest of the 88 modern constellations seen in the night sky.
‘Scorpius’ means the ‘creature with the burning sting’ in Latin.
Scorpius, also known as Scorpio (another Latin name) is quite easy to recognize, as it resembles the curvy body of a scorpion, if you join the dots and use your imagination.
Where is it located? –
Scorpius is positioned in the third quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere, south of the celestial equator. It is sometimes referred to being located in the SQ3 Quadrant.
Where can it be seen?
Co-ordinates of a right ascension, or left ascension and their declination are used to locate all of the Constellations, like Scorpius.
The Stars of Scorpius can be more easily observed from the Southern Hemisphere, on Earth, and also it can be viewed from the Northern Hemisphere, located between Sagittarius and Libra (the scales)
In the Southern Hemisphere
The Constellation of Scorpius is found at around 16 hours, 30 minutes right ascension and a 30-degree declination, in the Southern Celestial Sky.
The area of the sky where Scorpius is located is right in the center of the Milky Way.
Visibility from the Southern Hemisphere
It’s visible in the Southern Hemisphere at latitudes between +40 degrees and – 90 degrees and covers an area of 497 square degrees in the sky.
The other Constellations – Ara, Libra, Corona Australis, Lupus, Norma, Ophiuchus (sometimes referred to as the 13th constellation of the Zodiac), and Sagittarius border the Constellation Scorpius.
How can you identify Scorpius?
The simplest method for spotting any particular Constellationof the Zodiac from Earth is to first of all locate the brightest star in that Constellation, and then look at the neighboring illuminations, to see if you can identify a recognizable pattern.
Scorpius is represented as the scorpion and can be identified as an S shaped pattern, in the night sky.
Scorpius is a zodiacal Constellation located within the Milky Way and is visible as a faint band across the sky.
It has two bright Stars, Antares (the red supergiant) and the Shaula Star.
The Star System of Scorpius
The brightest star in Scorpius is called Antares (Alpha Scorpii).
It’s located approximately 520 light years from Earth and has a magnitude of 0.6 (which varies up to 1.6 to +5.5). Its luminosity is over 12,300 times brighter than the Sun.
FACT: It is the combined light of the various bright stars in this star system that produces enough light to give Antares (Alpha Scorpii) the brightest star status in the Constellation of Scorpius.
Spotting Scorpius in the night sky
The easiest way to spot the Constellation of Scorpius would be to locate the Bright Star Antares (Alpha Scorpii) in the Southern sky.
The next step is to try to imagine the surrounding shape of the starry scorpion, by joining the illuminated dots (the other bright Stars).
The two bright Stars, Shaula and Lesath form the imaginary tip of the Scorpion’s tail. They are collectively known as ‘The Stinger’, and appear as a double star to the naked eye.
Together, Shaula and Lesath are sometimes referred to as the ‘Cat’s Eyes”.
This simple technique can be used to spot other Constellation patterns too like the Scales (Libra) or the Goat (Capricornus).
The nameof the Brightest Star ‘Antares’ originates from the ancient Greek – anti Ares – meaning ‘the opposite of Ares’ or ‘the rival of Mars’.
As, ‘Ares’ is the Greek name for the planet ‘Mars’.
Antares has a distinctive reddish color when viewed by naked eye and was thought to rival the red color of the planet Mars. Hence the name, Anti Ares (rival of Mars).
Location
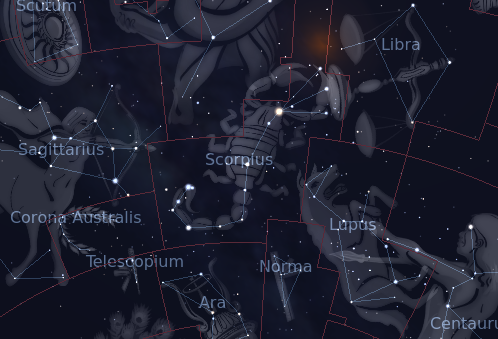
The Constellation Scorpiusis located between the Constellations Sagittarius and Libra and under Constellation Ophiuchus.
So, if you find the Constellation Sagittarius, then look across to the rightalong the ecliptic, until you see a curvy line, with The Stringer at the end, that’s Scorpius. If you look too far to the right and you’ve reached Libra!
FACT: The ecliptic is the imaginary line tracing the route that The Sun, the Moon, and the Planets take across the sky each year.
The Constellation of Scorpio, the Scorpion, is most prominent in the Northern Hemisphere, if looking South during July and August.
It remains visiblein the Northern Hemisphere until September.
In the Southern Hemisphere it will remain visible in the northern part of the sky until end of September.
The best time of day to spot it is at night, around 22.00.
Scorpius is at its highest in the sky in July and August when viewed from the Northern Hemisphere,but as time approaches the period when the Sun houses Scorpius, it begins to fade.
The Sun is in Scorpio from late October until late November.
When viewed from the below the equator, Scorpius appears upside down!
How is it formed and named?
The Constellation of Scorpius ranks as the 33rd largest in the sky and one of the biggest zodiacal constellations in the Southern Celestial Sky, and it fills an area of 497 square degrees.
It has a simple and easy to identify a shape like ‘a scorpion”.
It is formed by the positions of its 18 bright Stars forming the curving body that make up the Constellation of Scorpius.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU), has defined the boundaries of the Constellation of Scorpius as having dozens of stars that are visible by the naked eye.
The name Scorpius is abbreviated to ‘Sco’ by the IAU and as ‘Scor’ by NASA.
The main Stars in Constellation Scorpius
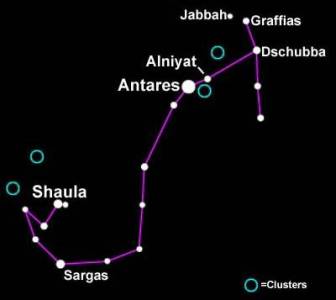
There are many different Stars within Scorpius.
The named stars of Scorpius are categorized by letters of the Greek alphabet, ranging in luminosity from the brightest Star, (the alpha star, the Antares, also known as Alpha Scorpii) then in decreasing order of luminosity through the alphabet.
- Antares (alpha Scorpii) the brightest Star in Scorpius, and a Red Supergiant. It is located around 38/70 light years from The Sun, and is hotter than the Sun)
- Shaula (lambada Scorpii) is the second brightest Star in Scorpius, and is actually a variable and multiple sub-giant star
- Sargas (theta Scorpii) is a variable bright giant star
- Larawag (epsilon Scorpii) is a variable giant star
- Dschubba (delta Scorpii) is a multiple hyper-giant star
The importance of the Constellation Scorpiuspre-dates the ancient Greeks.
It is one of the oldest known Constellations as was acknowledged as far back as the Babyloniansand the Sumerians who referred to it by thename Gir-tab, meaning the Scorpion.
Who, or what represents Scorpius? –
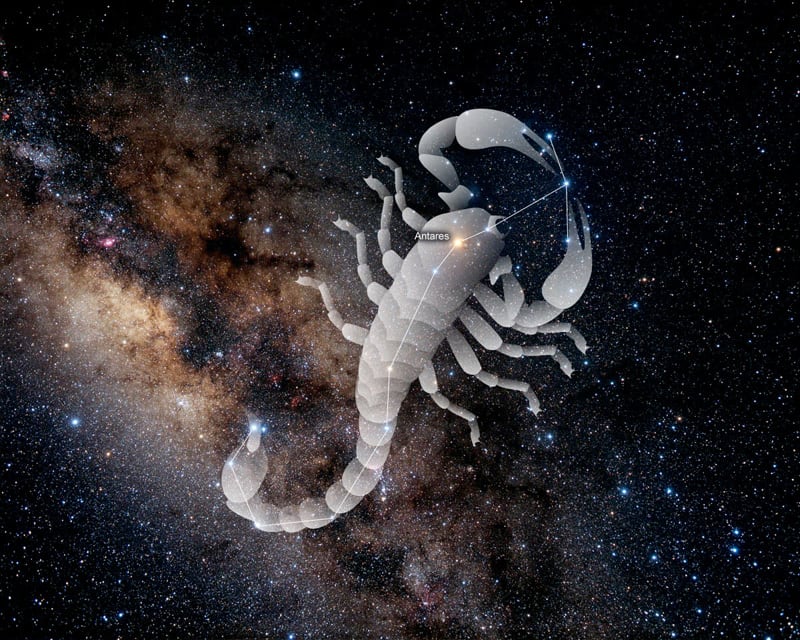

The Constellation Scorpius, is represented by – The Scorpion.
The reason is that it looks very similar to the outline of a scorpion with a curved tail (made up of the Stinger Stars).
How do the Bright Stars of Scorpius form the shape of a predatory arachnid?
The Bright Stars
If you look up and into the night sky you can imagine the recognizable outline of the Constellation of Scorpius, by the 18 bright Stars, which make up the outline of itsbody.
Stars with Planets
Scorpius has 13 Stars with known Planets orbiting around them in the solar system but they are unlikely to be able to support life forms.
Stars without Planets
Scorpius has further cataloged Stars with no planets.
The Constellation Scorpius a total of 15 main stars in its asterism. It also has 47 stars that are designated by Bayer Flamsteed.
Not all the stars within the Scorpius Constellation are visible to the naked eye but with telescopes and modern imagery techniques is it possible to glimpse all of the stars.
When was it first discovered? –
The ancient Greeks were the first ancient culture to name the 88 Constellations in the sky.
They were each given 3-letter abbreviations to help identify them and the Stars within those Constellations are also referred to by those 3-letter codes.
It was the Greek Astronomer – Ptolemy, who first cataloged the Constellation of Scorpius, in the 2nd Century (2 AD.). Ptolemy listed the various constellations in his Almagest (a book recording astronomical data).
When referring to a Star within a Constellation it is given the genitive form of the Constellation name. (‘Scorpi’ with ‘i’, giving Scorpii’).
FACT: In Latin, the genitive is the case of description.
The named Stars in Scorpius
Within the Constellation Scorpius, the Stars would be referred to by: the name or the letter from the Greek Alphabet, in order of brightness followed by ‘Scorpii’, (or their proper name) such as:
- Alpha Scorpii (Antares) – is the brightest Star in the Constellation, and the 15th brightest Star in night sky. It is a slow irregular variable Star, with an apparent magnitude of +0.6
- LambadaScorpii (Shaula, an Arabic name meaning the raised tail) – the second brightest Star in the Constellation and one of the brightest in the night sky overall and is a triple star system. It’s located around 570 light years from The Sun.
- Theta Scorpii (Theta Sco, or Sargas) – is a binary star with an apparent magnitude of +1.87and therefore one of the brightest visible Stars in the night sky, viewed from Earth. It’s located around 300 light years from The Sun.
- Delta Scorpii (Dschubba) – is a binary star that shows irregular slow brightness variations.
- Epsilon Scorpii (Eps Sco or Larawag) – is a giant Star, and suspected variable Star, with an apparent magnitude of +2.3. It is estimated to be around 63.7 light years from The Sun.
- Kappa Scorpii (k Scorpii, Gir-tab), – is a binary star system with an apparent magnitude of +2.4 and visible to the naked eye. It’s estimated to be located 480 light years from Earth.
- Beta Scorpii (b Scorpii, Beta Sco, or Acrab) – is a multiple star system, including Elacrab, Graffias, Grafias or Grassias. It appears as a binary Star when viewed by telescope, it is not visible to the naked eye.
- Upsilon Scorpii (u Scorpii, u Sco, or Lesath)is located in ‘the Stinger’ along with other bright StarLambada Scorpii, forming an optical pair referred to as the ‘Cat’s Eyes’.
- Tau Scorpii – (Alniyat, Paikauhale or Al Niyat) a Star with an apparent visual magnitude of +2.8
- Pi Scorpii – a triple Star System, (Fang, Nur and Vrischika) combined magnitude of 2.9
- SigmaScorpii – a multiple Star System, (Alniyat, Al Niyat and b Scorpii) combined apparent magnitude of +2.88
- Iota Scorpii – (Apollyon) a Star with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.03
- Mu Scorpii – (Xamidimura, Denebakrab) a binary Star System, a Star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +3.04
- G Scorpii – (y Tel, Fuyue) a giant Star, apparent magnitude +3.19
- Eta Scorpii – a Star (suspected variable Star)with an apparent magnitude of +3.33
- Mu2 Scorpii – (Pipirima) a Star with an apparent magnitude of +3.56
- Zeta 2 Scorpii – a K-type orange giant star, located near theblue-white supergiant Star Zeta Scorpii,with an apparent magnitude of +3.59 – 3.65
- Rho Scorpii – (Lklil) a double Star, with an apparent magnitude of +3.87
- Omega1 Scorpii – (Jabhat al Akrab) a Star with an apparent magnitude of +3.95
- Nu Scorpii – (Jabbah, Jabah) multiple Star system, with an apparent magnitude of +3.95
- H Scorpii – a Star with an apparent magnitude of +4.18
- N Scorpii – (alpha Nor) a Blue GiantStar with an apparent magnitude of +4.23
- Q Scorpii – an Orange GiantStar with an apparent magnitude of +4.27 (located in the tail of the Scorpion, between Lambada Scorpii and Upsilon Scorpii)
- Omega2 Scorpii – (Jabhat al Akrab) a suspected variable Star with an apparent magnitude of +4.320
- 13 Scorpii – a binary Star with an apparent magnitude of +4.57
- 2 Scorpii – a double Star with an apparent magnitude of +4.69 (its fainter Star has a magnitude of +6.98)
Fact: the brighter the luminosity of the star the lower the apparent magnitude number.
The Constellations change their positions throughout the year as the Earth rotates around the Sun.
This means our position in space is forever changing and as a result our view of what’s in space changes too, and will continue to do so.
Why and what is the purpose of Scorpius? –
In ancient times the dots, bright lights and perceived objects in the sky were of great interest and the makings of folklore to a great range of people from seamen to farmers.
From children to the elderly, we have had an ongoing fascination, with our solar system and star system. Perhaps it’s because the enormity and variety within it makes us realize just how large and exciting the universe is.
FACT: The Star System or Stellar System is a small number of stars that orbit around each other and are bound together by gravity.
When it becomes a large group of stars, again bound together in the same way, by gravity, it is known as a Galaxy or Star Cluster.
Whether they contain small groups of stars or larger groups of stars they both come under the classification of ‘Star System’.
The Constellations in the night sky were a useful navigation tool and guide as well as the subject of legends and myths, about Zodiac characters like Zeus, Orion and other powerful gods.
42 of the Constellations have been named after animals with a story behind each name.
Background & Facts:
Part of the Zodiac
The Constellation of Scorpius (Scorpio) found in the Southern Sky, is one of the largest constellations of the zodiac.
When the zodiac ‘ring’ or ‘belt’, of constellations is listed in order, as the 12 astrological zodiac signs (months) of the calendar from January to December, it lists as:
- Capricorn; Aquarius; Pisces; Aries; Taurus; Gemini; Cancer; Leo; Virgo; Libra; Scorpio and Sagittarius
In the order of the vernal equinox (where the ecliptic meets the celestial equator) the order of the signs begins with Aries, the first, and then and runs through to Pisces. In this series Scorpio is the 8th sign of the Zodiac.
However you categorize the list of the Constellations of the Zodiac, each Constellation in the belt, like Scorpio, has two immediate Constellation neighbors – one in front (e.g. Sagittarius is in front of Scorpio) and one behind it (e.g. Libra is behind Scorpio).
Hiding in the house
The constellations in the Zodiac ‘belt’ form an imaginary ring that’s closely aligned to the orbit of Earth.
As a result each of the 12 zodiac constellations has a cycle that passes through the Sun (the biggest and brightest Star, that is actually a Dwarf Star not a Giant Star).
The Sun is then said to house (hide) each Constellation in turn, a different Constellation each month. At that time you cannot see that particular Constellation.
The Sun passes through the sign of Scorpio between October 23 and November 21.
This is about one month before the Sun passes through the Scorpius constellation. At this point Scorpio would be referred to as hiding in the house of Scorpio.
The neighbors of Constellation Scorpius
The Constellation of Scorpius is neighbored by several constellations in the southern Sky: Constellation Sagittarius is the guide point for finding Scorpius in the sky.
The other neighbors include Ara, Corona Australis, Libra, Lupus, Ophiuchus, Norma and Sagittarius.
Within Constellation Scorpius
The Constellation of Scorpius is formed by of a number of different components.
The different components housed by the Constellation Scorpius are mainly Stars, Deep Sky Objects and Messier objects (galaxies).
The best time of year to see the Stars and Deep Sky Objects in Scorpius is July.
Stars
There are many different types of Stars in the star system categorized by size, lifespan and luminosity.
Generally, larger Stars have a shorter lifespan.
Stars are formed from clouds of interstellar gas and include:
Red Dwarf Stars
Most of the stars in the galaxy are Red Dwarf Stars. They are small in size measuring about 40-50% of the mass of The Sun. They are cool and their luminosity has only about 10% of the brightness of the Sun (our brightest Star), and they live for longer.
Brown Dwarf Stars
These are known as failed stars that form like other stars but don’t reach the mass, heat or density to begin the nuclear fusion process. They are only about 8% of the mass of the Sun and are red not brown, and not easy to spot in the night sky.
Red Giant Stars
These are giant luminous stars that have a low or medium mass. A Red Giant Star is formed when a star expands its volume by fusing all of its hydrogen into helium, and then burning the helium to produce carbon and oxygen to expand.
Blue Giants
These are giant, bright stars that range from 10-100 times the size of the Sun and are 1000 times brighter. They are big and hot and therefore burn out quickly. The biggest are called Blue super giants or hyper giants. The biggest ever discovered was about 10 million times brighter than the Sun,
Yellow Dwarfs
These are main-sequence stars like the Sun, but only 80% of its size, and are bright stars,
White Dwarfs
These are small burnt out husks of stars, about the same size as the Earth. White Dwarfs are dense and represent the final state of evolution for a star, like most stars in the galaxy.
Black Dwarfs
These are the remains of a White Dwarf after it cools and darkens. This is likely to happen after about 10 billion years of life.
White Stars
These are also main-sequence stars like the Sun, but twice the size, and are bright stars and hot.
Other types of stars include the Orange Giant, Neutron stars, Variable Stars and Binary Stars
Bright Stars
The sky is home to various bright stars.
The brightness of a star is measured by a value called its magnitude and they come in different sizes, composition, mass and color. Their vast distance away from us is measured in light years from either the Earth or the Sun.
The lower the magnitude value the brighter the star appears in the night sky when viewed from Earth.
FACT: The Sun is considered to be the brightest star in the sky.
Scorpius has 13 named stars that host planets within the Constellation Scorpius that have been officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU):
As well as Stars, the Scorpius Constellation also has deep sky objects and galaxies (or even globular clusters or open clusters).
Deep Sky Objects
FACT: A Deep Sky Object is an astronomical object, that is not a solar system object like the Sun, Moon, Comet or a Planet. An individual Staris not considered to be a Deep Sky Object.
Deep Sky Objects are faint objects that can still be observed by the naked eye in the night sky from Earth.
They include Galaxies, Star Clusters and Nebulae.
What is a Nebula?
A Nebula is a massive cloud of gas and dust in Space.
Some Nebulae are formed when a star explodes and then dies, as is the case with a Supernova. Sometimes they can act as Star nurseries and are the areas where new Stars are forming.
The Nebulae are the spaces in between the stars referred to as interstellar space.
Images of the Nebulae have been captured using professional Space telescopes, such asthe NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, operated by NASA, and the famous Hubble Space Telescope.
Nebulae in Scorpius include:

NGC 6302 – the Butterfly Nebula. This is a bipolar planetary nebula.
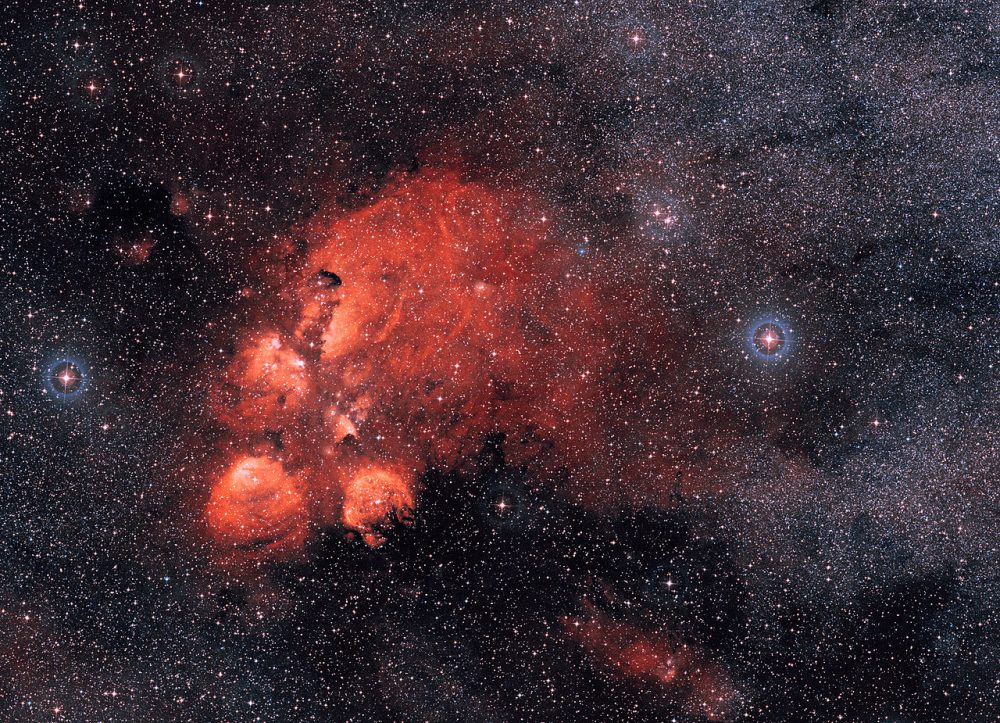

NGC 6334 – the Cat’s Paw Nebula

NGC 6357 – the War and Peace Nebula. This is a diffuse nebula with lots of proto stars.

NGC 6231 – Caldwell 76, is an open cluster, 5,900 light years from the Sun, and half a degree north of Zeta Scorpii.
Messier Objects and Star Clusters
There are four Messier objects within the Scorpius Constellation:
- Messier 4, Messier 6, Messier 7 and Messier 80
Charles Messier

Charles Messier, a French astronomer, is credited with identifying various objects in the night sky, around 1764.
He is famous for publishing the Charles Messier astronomical catalogue that lists 110 nebulae and star clusters.
These later became known as the Messier objects.
Messier 4 (M4) is a bright globular cluster found in Scorpius. This globular cluster is some 7,200 light years from Earth.
It has an apparent magnitude of 5.9 and the designationof NGC 6121 within the Messier ‘New General Catalogue’.
Messier 6 (M6), the Butterfly Cluster, is a bright open cluster found in Scorpius. This cluster is some 1,600 light years from Earth.
Robert Burnham, an American Astronomer thought this arrangement of Stars looked like the outline of a Butterfly with open wings.
He therefore named M6 – The Butterfly Cluster.
It has an apparent magnitude of 4.2 and the designationof NGC 6405 within the Messier ‘New General Catalogue’.
Messier 7 (M7), Ptolemy’s Cluster, is a bright open cluster found in Scorpius. This cluster is some 980 light years from Earth, and visible by the naked eye.
It has an apparent magnitude of 3.3 and the designationof NGC 6475 within the Messier ‘New General Catalogue’.
Messier 7 can be found near the Stinger on the outline of the celestial Scorpion and is the most southerly Messier Object within Scorpius. It may therefore be a tricky object to spot from Northern latitudes.
Messier 80 (M80) is a globular cluster found in Scorpius. This globularcluster is some 32,600 light years from Earth and is considered to be one of the most densely populated global clusters in the galaxy.
It has an apparent magnitude of 7.87 and the designationof NGC 6093 within the Messier ‘New General Catalogue’.
It can only be seen by telescope, located between the 2 brightest Stars in Scorpius – Antares (Alpha Scorpii) and Akrab, also known as Graffias, (Beta Scorpi)
The best time to view it is in summer.
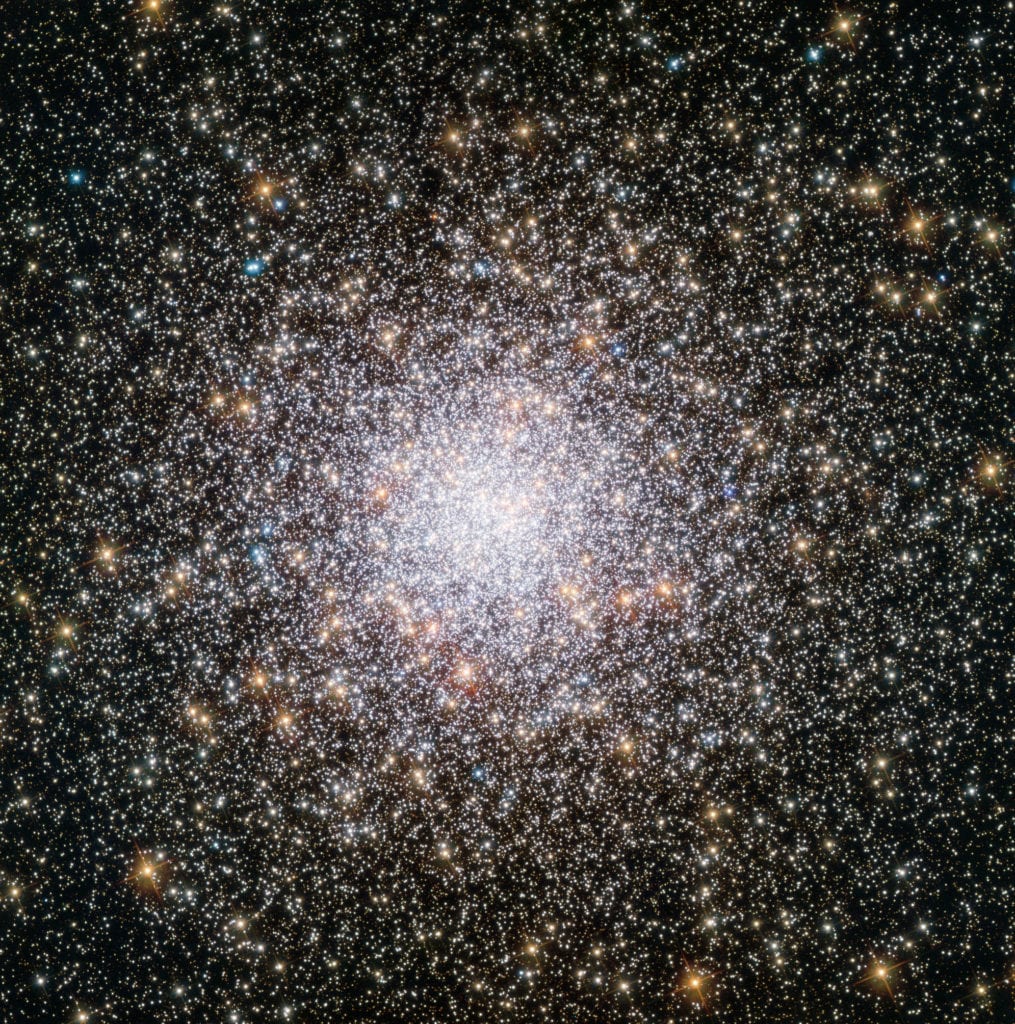
FACT: A star cluster is a large group of Stars, of which there are 2 different types:

-
Globular Clusters:
A global cluster is a spherical collection of ‘Old Stars,’ numbering hundreds to millions, that are tightly bound by gravity and orbits a galactic core.

-
Open Clusters:
An open Cluster is a looser formation of ‘Young Stars’ that generally has less than a few hundred Stars.
What is the Milky Way?
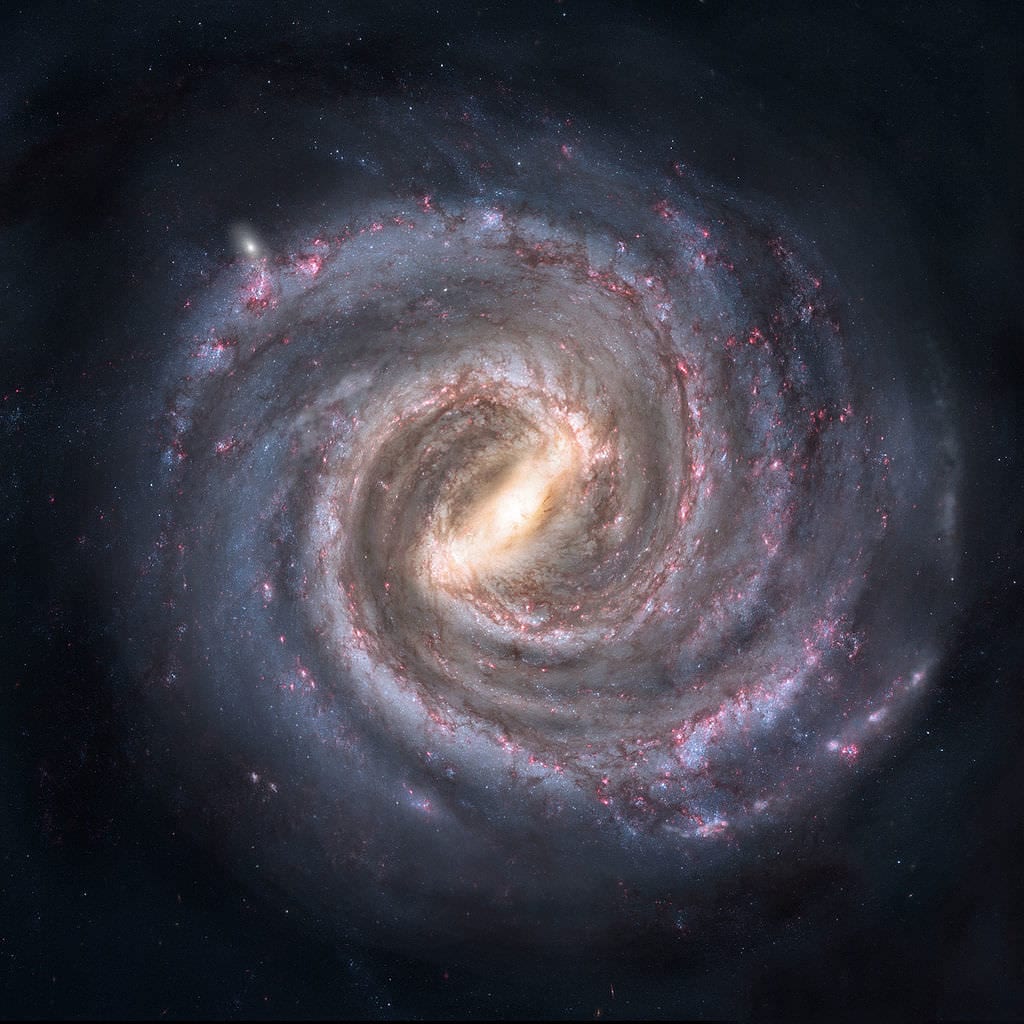

The Milky Way is a Spiral Galaxy, containing over 200 billion Stars, and actually forms part of the Constellation of Sagittarius.
The Milky Way itself is not a Constellation of Stars. It is the Galaxy that contains our solar system and it gets its name from the fact that it looks like a hazy swirl or river of milk across the sky, when viewed from earth. It is made up of gas, dust and stars, with spiral arms wrapped around it, and a massive black hole in the center of the Galaxy.
Not all of the Stars in the Universe are contained within the Milky Way. It is at its brightest if looking towards the galactic center in the direction of Sagittarius.
The Stars that make up the Milky Way are many light years away and cannot be individually identified by the naked eye.
Historical significance: the legends, and myths surrounding Constellation Scorpius
Myths
When it comes to the many recognized constellations in the sky, Constellation Scorpius is one of the oldest known in the Zodiac.
Scorpius was one of the first 48 Constellations listed by Ptolemy, the Greek/Roman astronomer.
Greek mythology
There are many Greek myths and legends surrounding the origin and names of the constellations, involving Zeus, and the death of Orion the Hunter, and even mythical creatures.
For thousands of years, various cultures around the world have identified and named the constellation we know and see in the night sky as Scorpius.
The Babylonians also recorded details of variousbright stars within the constellations in their Babylonian star catalogues before 100BCE. They called Scorpius, the creature with the burning sting.
The myth of Scorpius
In Greek Mythology, Orion the human Hunter was strong, powerful and determined to win at any cost.
He attracted the attention of Artemis, the goddess of hunting and survival, and boasted that he was the man of all gods and could kill any animal in their world.
This announcement concerned Gaia, the goddess of the Earth, so she created a giant scorpion to kill him. In the attack, Orion swung his sword at the scorpion but it impaled him.
Artemis tried to help him and fired an arrow at the scorpion but it hit Orion in the leg instead.
When Orion died, Artemis returned to her god family and the scorpion’s reward was to become stars in the sky, as was Orion.
What is the difference between a constellation and an asterism?
An asterism is a group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the night sky but with no officially determined boundaries.
It can make up part of a constellation or cross the boundaries of an official constellation or even a defunct constellation.
An asterism is a more vague assembly of stars than a recognized constellation.
The Zodiac sign of Scorpio

The constellation of Scorpius is one of the 12 constellations of the Zodiac and as such is represented by the birth star sign of Scorpio.
Scorpio is a Water sign.
We know what Scorpius looks like in the night sky in the Southern Hemisphere but what are the typical personal characteristics of someone born under the zodiac sign of Scorpio?
Characteristics of Scorpios
The Star sign of Scorpio includes people born between, October 23 to November 21.
Scorpio is one of the 4 ‘Fixed’ signs of the Zodiac: Taurus, Leo, Scorpio and Aquarius. They are sometimes referred to as the ‘Fixed houses’’.
It is believed that people born under one of these signs will have certain traits and behaviors.
Scorpio people
The typical characteristics of a Scorpio person, is related to having a steadiness, stability and purpose to achieve their objectives.
Negative traits: They can be stubborn and give few second changes with a sting in their tail when provoked!
Positive Traits: They are reliable, stable and love to get things done.
The meteor showers

The Scorpius Constellation is associated with 2 meteor showers known as ‘The Scorpiids’.
The 2 meteor showers are:
- The Alpha Scorpiids
- The Omega Scorpiids
The Alpha Scorpiids meteor shower occurs between April 21 and May 26, with its peak on May 15 each year.
Fun Facts about Scorpius – Did you know that?
- The proper astronomical name is Constellation Scorpius as distinct from the name ‘Scorpio’ which is its corresponding name of the astrological sign of the Zodiac, and is symbolized by the Scorpion.
- The Constellations are not part of the solar system; they are groups of stars that appear to form shapes that are visible from Earth.
- The largest Constellation is called Hydra and the smallest Constellation is called Crux.
- The Sun does not belong to any constellation.
- A Constellation does not actually exist as a fixed object, it is a group of bright stars that happen to be in a random place and are light years apart and ever moving. We see the pattern of their presence.
- In Hawaii, the Constellation Scorpius is called the demi-god Maui’s fishhook
- In Babylonian times it was called MUL.GIR.TAB, meaning the creature with the burning sting
- In Indonesia, the Javanese people refer to Scorpius as the leaning coconut tree or the brooded swan.
- The center of a Galaxy does not contain a Giant Star it contains a massive Black Hole.
- Red Dwarf is not a Dwarf Planet it is a Star. Most common Stars are Red Dwarf (cool Stars)
- Spiral Galaxies make up about two third of all the Galaxies in the Universe
- In ancient Babylonian descriptions, the part of the Scorpion that would represent the celestial claws of the Constellation of Libra
Commonly Asked Questions
Q. What is the celestial sphere?
A. In astronomy and navigation terms, the celestial sphere is imaginary.
This virtual sphere has a large radius that is concentric with Earth.
We can imagine all objects in the night sky as being projected upon the inside of this celestial sphere, as if it was images placed inside a dome.
Q. What prevents us seeing the Stars and Constellations in the night sky?
A. Light pollution, fog, city lights and artificial lights all limit our visibility of the objects in the sky at night.
The best views come from outside of cities where light pollution is less. Camping in the countryside is one of the best ways to get a better view of what’s up there in Space.
Q. Will the Constellations change over time?
A. The Constellations are continually on the move.
The images we form in our imagination to make objects, shapes and patterns out of the constellations have already shifted over time.
As we view the night skies from Earth they are likely to continue to do so and possibly in time the images may look very different.
SOURCES:
- https://vocal.media/futurism/finding-scorpius-constellation
- https://in-the-sky.org/data/constellation.php?id=74
- https://nineplanets.org/scorpius-constellation
- https://www.astronomytrek.com/scorpius-the-scorpion
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGC_6302
- https://www.constellation-guide.com/cats-paw-nebula
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGC_6357
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGC_6231
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Messier
- https://astronomynow.com/2016/10/24/hubble-reveals-ngc-362-a-young-globular-cluster
- https://www.wikiwand.com/en/List_of_open_clusters
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Milky_Way_Galaxy.jpg
- https://www.almanac.com/content/scorpio-zodiac-sign
- https://www.gettyimages.ca/detail/photo/meteor-showers-and-the-milky-way-royalty-free-image/1020811292?adppopup=true